 The “sharing economy.” It’s the new, new thing (or, depending on your perspective, very, very old). Over the past five years, companies like Uber and Airbnb have attracted millions of dollars of venture capital and built a huge customer base. “Just as peer-to-peer businesses like eBay allow anyone to become a retailer,” The Economist writes, “sharing sites let individuals act as an ad hoc taxi service, car-hire firm or boutique hotel as and when it suits them.” The ability to share goods and services is having a disruptive impact across the economy. Can energy be far behind?
The “sharing economy.” It’s the new, new thing (or, depending on your perspective, very, very old). Over the past five years, companies like Uber and Airbnb have attracted millions of dollars of venture capital and built a huge customer base. “Just as peer-to-peer businesses like eBay allow anyone to become a retailer,” The Economist writes, “sharing sites let individuals act as an ad hoc taxi service, car-hire firm or boutique hotel as and when it suits them.” The ability to share goods and services is having a disruptive impact across the economy. Can energy be far behind?
NEWS: Does Energy Have a Place in the Sharing Economy?
Topics: News Update
 In a press conference Thursday afternoon, Nevada Governor Brian Sandoval and Tesla Motors CEO Elon Musk announced that the company’s groundbreaking battery manufacturing facility (called a “Gigafactory”) will be located in Nevada. Shortly after Tesla announced plans to build the Gigafactory in February, several states in the southwest scrambled to compete for the final location. Arizona, Texas, California, and New Mexico gambled for Tesla’s favor, but the house always wins in Nevada.
In a press conference Thursday afternoon, Nevada Governor Brian Sandoval and Tesla Motors CEO Elon Musk announced that the company’s groundbreaking battery manufacturing facility (called a “Gigafactory”) will be located in Nevada. Shortly after Tesla announced plans to build the Gigafactory in February, several states in the southwest scrambled to compete for the final location. Arizona, Texas, California, and New Mexico gambled for Tesla’s favor, but the house always wins in Nevada.
Topics: News Update
NEWS: Verizon Teams with SunPower; UBS Touts EVs and Storage
 Until recently, investors have looked askance at “corporate sustainability” efforts, viewing them as more public relations than investment, and environmental advocates sometimes seeing them as less than sincere (“greenwashing”). But more and more, corporate investment in advanced energy is going straight to the bottom line. Case in point: the deal announced this week between two AEE members – Verizon and SunPower.
Until recently, investors have looked askance at “corporate sustainability” efforts, viewing them as more public relations than investment, and environmental advocates sometimes seeing them as less than sincere (“greenwashing”). But more and more, corporate investment in advanced energy is going straight to the bottom line. Case in point: the deal announced this week between two AEE members – Verizon and SunPower.
Topics: News Update
NEWS: Nearly 100% of New Generating Capacity This Year is Advanced Energy
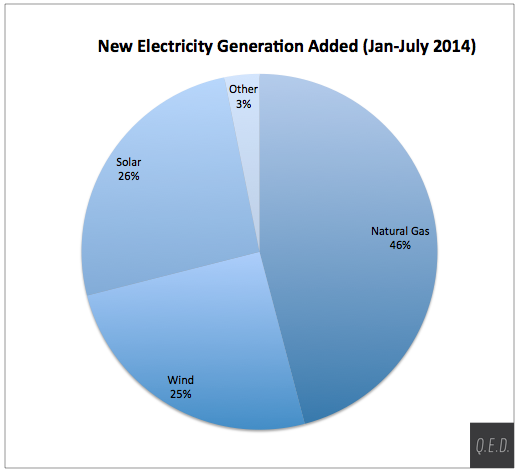
Advanced energy is on the march. A new report from the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) shows that, of all the new electric generating capacity installed in the U.S. since January, more than 97 percent was advanced energy: 46 percent natural gas, 26 percent solar, and 25 percent wind. The remaining 3 percent of new capacity shown as “other” in the accompanying chart includes 87 megawatts of biomass, 32 MW of geothermal steam, and 19 MW of hydro. That means, in fact, that 99.7 percent of the 4,758 MW of new generating capacity added in the first seven months of the year was advanced energy – 11 MW of oil-fired generation and 1 MW of truly “other” accounted for the remainder. In July, all the new capacity that month came from wind (379 MW) and solar (21 MW). The FERC numbers count only utility-scale installations, and do not include solar installed on residential and commercial rooftops.
Topics: News Update
NEWS: As Coal Declines, U.S. Poised for Leadership in LNG Exports
 Just last year we noted that the U.S. was uniquely poised to become a major exporter of liquid natural gas (LNG). This week we saw another step in that direction as the Department of Energy (DOE) announced that it had conditionally authorized Oregon-based LNG Development Co., LLC (Oregon LNG) to export LNG to countries without a Free Trade Agreement with the U.S. Oregon LNG would export the domestically produced gas from its terminal in Warrenton, Oregon. The facility is authorized to export up to 1.25 billion standard cubic feet of LNG per day for the next 20 years, though the project is subject to final regulatory authorization and environmental review.
Just last year we noted that the U.S. was uniquely poised to become a major exporter of liquid natural gas (LNG). This week we saw another step in that direction as the Department of Energy (DOE) announced that it had conditionally authorized Oregon-based LNG Development Co., LLC (Oregon LNG) to export LNG to countries without a Free Trade Agreement with the U.S. Oregon LNG would export the domestically produced gas from its terminal in Warrenton, Oregon. The facility is authorized to export up to 1.25 billion standard cubic feet of LNG per day for the next 20 years, though the project is subject to final regulatory authorization and environmental review.
Topics: News Update