This post is one in a series featuring the complete slate of advanced energy technologies outlined in the report This Is Advanced Energy.
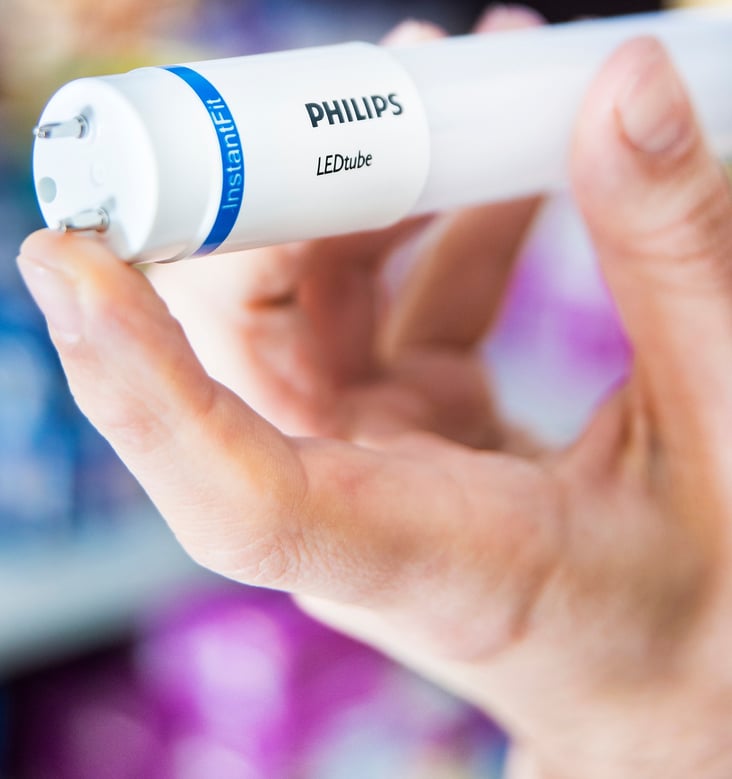

Lighting accounts for 20% of energy use in commercial buildings and 10% of energy use in residential buildings. Installing efficient lighting is one of the lowest cost, fastest payoff energy efficiency improvements available today. Advanced lighting technology includes light-emitting diodes (LEDs), energy-saving incandescent bulbs, and compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs). LEDs, especially, are transforming lighting markets today — once limited to niche applications, they can now be used in virtually any lighting application. LED lighting is five to six times more efficient than incandescent bulbs and up to 1.5 times more efficient than CFLs. LEDs are typically dimmable and especially well suited for use with intelligent lighting controls, which use sensors to collect environmental information (such as occupancy or ambient light) and automatically adjust light levels, cutting lighting energy use by 80% to 90%. The market for high-efficiency bulbs is well developed, with demand for conventional incandescent lights dropping by half from 2007 to 2012 as efficient bulbs have come to dominate the market.