This post is one in a series of feature stories on trends shaping advanced energy markets in the U.S. and around the world, drawn from Advanced Energy Now 2015 Market Report, which was prepared for AEE by Navigant Research.

Industrial companies that have high energy consumption rates can benefit immensely from understanding and managing energy consumption within their facilities and throughout the entire enterprise. The implementation of an industrial energy management system (IEMS) has become critical to this understanding. An IEMS provides the capability to bring information and knowledge of all aspects of energy-related matters into the present, where cost-effective tactics can be employed to reduce inefficiencies and avoid high demand charges.
Large equipment manufacturers such as Schneider Electric, Siemens, Invensys, and Rockwell Automation have been leading suppliers to this market for a long time. The landscape is shifting, though, and large IT companies like SAP and IBM are becoming more influential, due to their capability for handling large datasets and their experience with enterprise-level business analytics. Smaller niche companies are also participating in the IEMS market with unique product and service offerings, often in partnership with larger, more established vendors to gain access to the market.
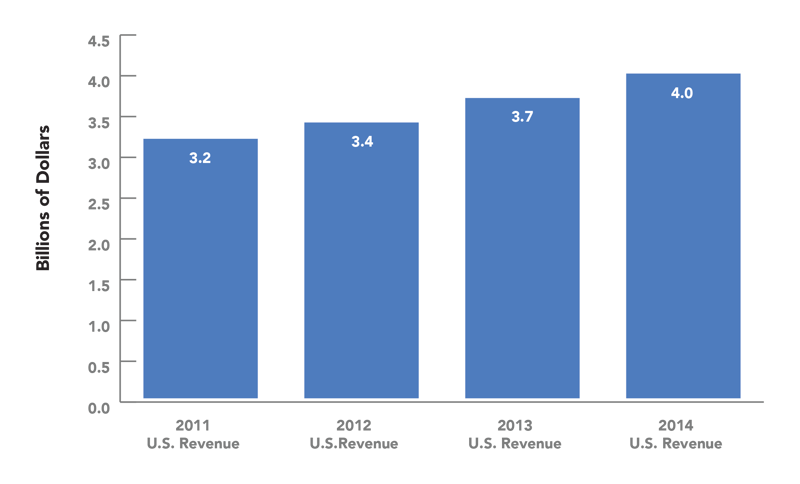
Global IEMS revenue across software and services was $12.3 billion in 2014, up 9% over 2013 and 26% over the past four years. The total IEMS market in the United States grew to just under $4 billion in 2014, 8% over 2013 and 25% compared to 2011. The North American market (of which the United States represents around 90%) is the largest region for IEMS revenues globally, with a slim lead over Europe. Though U.S. industrial companies have been relatively conservative in spending during the recent recession, more robust investment in IEMS is expected as companies look to meet competitive challenges and start to assimilate new innovations, enter new capital spending cycles, and recover from earlier contraction. That’s because inefficient energy use carries with it heavy penalties, in the form of high costs from excess energy consumption and onerous utility demand charges.
A number of trends are driving the evolution of industrial energy management systems and offer significant opportunities for new and existing data-driven companies to optimize energy consumption for the world’s most energy intensive sectors. One is the wave of innovation driven by machine-to-machine technologies that are underpinning the emergent “Internet of Things.” Communication networks and intelligent devices are creating a greater level of connectivity and delivering new insight into industrial operations. The industrial Internet of Things comprises machine learning software, data analytics, intelligent sensors, and machine-to-machine (M2M) communication technology that can capture data from machines, process it, and use it to adjust operational characteristics or performance. Machine-to-machine communications are not new in industrial facilities but they are now reaching a level of complexity and scale that changes the degree of insight and control available.
The finer grained control and deeper insight into performance offered by intelligently connected systems also enable finer tuning of energy management programs. However, further work needs to be done on the standardization of protocols for industrial communications and integration. In the United States, this is an area of focus for the National Institute of Standards and Technology, which is working on a number of programs to support smart manufacturing, with industry support.
An associated area of innovation is the use of advanced analytics to improve energy efficiency in industrial operations. Better forecasting and predictability connected to energy-related sourcing and consumption can provide another level of improvement in energy management. Forecasting is beneficial in an industrial setting for materials and resource management, better use of production facilities, cost avoidance, and a host of other areas. However, creating a standard approach to energy forecasting in highly variable use situations is a difficult proposition.
Other improvements are being made by focusing on immediate circumstances and delivering real-time information that can allow for continuous optimization in current operations. Faster processing speeds and inexpensive storage have allowed big data to be processed and served up to users in real-time, or near real-time, on the floor of an industrial facility. Operators can now see important aspects of production processes as they are happening, allowing for adjustments on the fly, as incremental improvements can add up to big savings over time. Built-in alerts tailored to a specific facility or process tell operators when critical adjustments need to be made. Over time, the automation of the process, based on historical analysis and rules-based intervention, can eliminate human error and make minute efficiency-related adjustments while the process is running.
More generally, the lines between the production and corporate environments are blurring. IEMS vendors are elevating the reporting of energy-related data to the enterprise level. They are providing more detailed visibility into operational metrics in a format that is understandable and useful to any level of an organization. Energy-related data and information have traditionally been the responsibility of personnel who were closest to its use, while the cost of energy (along with payment for it) was relegated to the accounting function – many times when the energy bill was received. Now this information is available to a variety of enterprise functions in real-time for an ongoing and up-to-date holistic view of the organization.
Energy is fast becoming another input that needs to be managed on a proactive basis, utilizing the most up to date data available. As IEMS products and services become ever more sophisticated, energy data can be combined with other business intelligence data to provide a more complete and actionable picture of overall business performance.
Download the full Advanced Energy Now 2015 Market Report to learn more about the current size and scope of the advanced energy economy.
Featured image courtesy of surber.
